Ikalawang yugto: Basihang kaalaman ukol sa tilapya
Ang tilapya ay unang dinala sa Pilipinas noong 1972, naging mabilis ang pagsikat nito dahil sa dali nitong padamihin, mabilis na paglaki, pagiging masarap, pagiging malakas ang resistensya sa sakit, at ang pag-angkop nito sa iba't ibang uri ng klima, temperatura at alat.
URI NG TILAPYA
Genus Tilapia (Substrate spawners)
Both parents guard, protect, aerate the breed, and help move clutch to different nest sites. Fry at first feeding are 4-5 mm and show feeble swimming ability. Fry survival relatively low.
Genus Sarotherodon (Paternal/biparental)
Both parents stay close to each other. Eggs and fry brooded in oral cavity up until they are ready for release. Brood may not be collected once released. Fry are between 7-9 mm at first breeding, well developed fins for swimming. Fry survival high.
Genus Oreochromis (Maternal)
Female solely involve in brood care. After spawning, female leaves nest to rear her clutch in safety. Fry brooded up until free swimming. There is an extended period of care during which fry seek shelter in buccal cavity for safety. First feeders have well-developed fins for swimming. Fry survival high.
PAGKILATIS NG KASARIAN
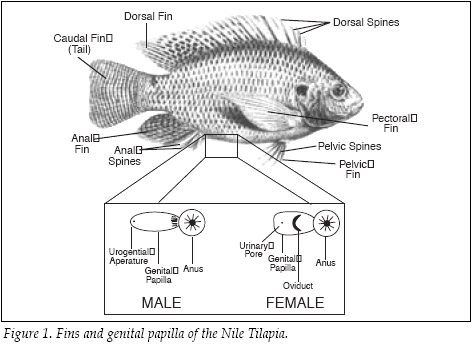
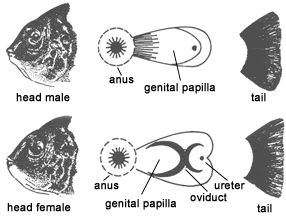
madali ang pagkilala kung ang tilapya ay babae o lalaki, Ang lalaki ay may dalawang butas just in front of the anal fin. at ang babae ay may tatlong butas. Kung ang isda ay 15 gramo na maaari na itong makita.
Sex identification of tilapia is relatively simple. The male has two openings just in front of the anal fin. The large opening is the anus and the smaller opening at the tip is the urogenital pore. The female has three openings: the anus, the genital pore, and the urinary pore. The genital papilla is usually smaller in the female. Tilapia can be sexed when it has attained the weight of 15 grams. Application of ink or dark dyes to the papillae may increase the accuracy of sexing and may allow sexing of smaller fish. By rubbing ink along the papillae of the tilapia, sexes can be readily distinguished.
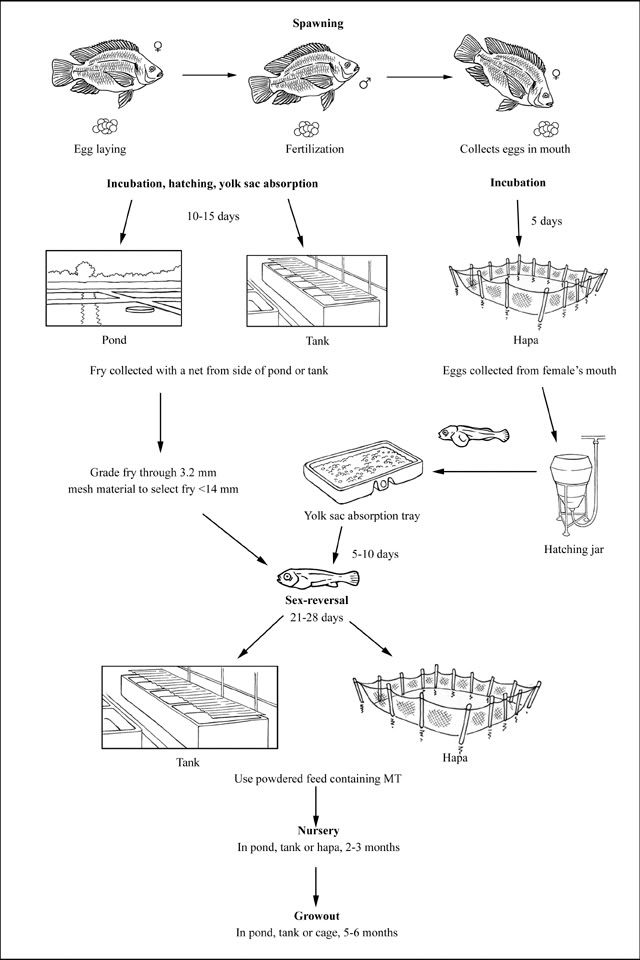
PAGPUPUNLA/ PAGPAPARAMI
The
Females spawn every four to six weeks, but may spawn sooner if the eggs are removed. The number of eggs per spawning is related to the size of the female. A female of about 100 grams may produce approximately 100 eggs per spawning while a female of about 100 to 600 grams can produce approximately 1,000 to 1,500 or more eggs per spawning.

2 Comments:
ano po ang pinagkaiba ng tilapyang alat at tilapyang tabang? ung tilapyang alat po ba ay nabubuhay sa seawater at ang tilapyang tabang sa ilog or lake?
By Loi0180, at 7:57 PM
Loi0180, at 7:57 PM
Tama po kau. Ganun nga po.
By Unknown, at 1:51 AM
Unknown, at 1:51 AM
Post a Comment
<< Home