fish food requirements
FAT: 4-28 %
CARBOHYDRATES 10-30%
VITAMINS 1:0-2:5 %

1. Substrate kahit alin dito
manure + ipil-ipil or kakawate (2:1)
rice straw + manure (1:1)
grasses + chicken manure (3:1)
sawdust + ipil-ipil (3:1) compost / rice straw + corn barn (1:1)
cardboard and paper pulp
(basurang nabubulok, wag lalagyan ng kahit anong uri ng plastic)
Paraan: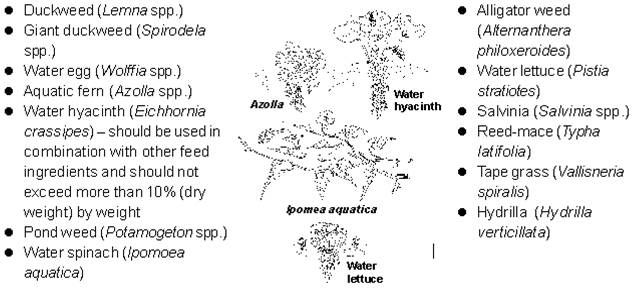







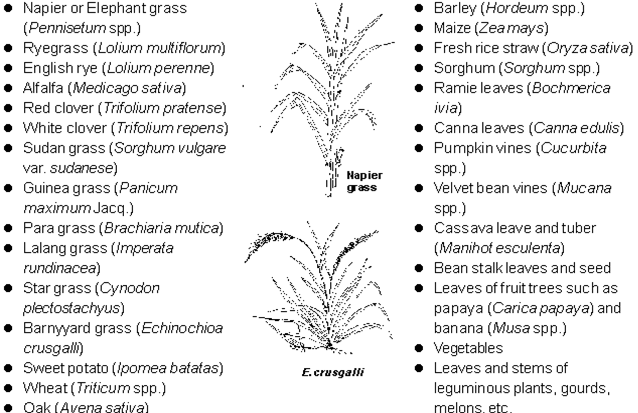
Commonly used terrestrial plants (CP 10-30%, FCR 20-50)












B. Aquatic animals and terrestrial-based live feeds (CP 40-85%, FCR 10-80)
Aquatic animal feeds and terrestrial-based live feeds are considered to be nutritionally complete. Terrestrial-based live feeds such as earthworms and maggots can be produced on-farm using various organic wastes. Some examples are:
· mollusks such as snails and clams;
· insects such as silkworm larvae (Bombyx mori), soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) and termites (Reticulo termes santonesis and Zootermopsia nevadensis);
· small crustaceans such as wild small shrimp; and
· earthworms and maggot